
IT Master Plan: How to make it a success?
This article is a follow up to the previous article “The IT audit, a good investment”, in which we can learn about the IT audit process and how this IT audit step represents the essential prerequisite for an IT master plan.
The IT master plan is one of the main catalysts for the success of organizations in implementing best IT management practices and digital transformation elements. It is essential to implement an IT master plan focused on the activities that correspond to the needs of your organization.
This article is designed to help you think about your priorities, to align strategic IT initiatives with your organization’s goals and core values, to apply a continuous improvement process to IT practices and to monitor and update your organization’s IT master plan.
The IT master plan essentially lays out an organization’s IT priorities or guidelines for the next two to three years.
The procedure
The method proposed here follows steps 1 and 2 of the IT audit. To achieve the master plan, there are three steps:

Figure 1 – IT Master Plan process
Step 3: Analysis
During the IT audit stage of the CIO 360 approach, we were able to assess the best practices for each theme, allowing us to qualify the elements of maturity vs criticality for the organization. The analysis then made it possible to summarize the indicators according to the following table:
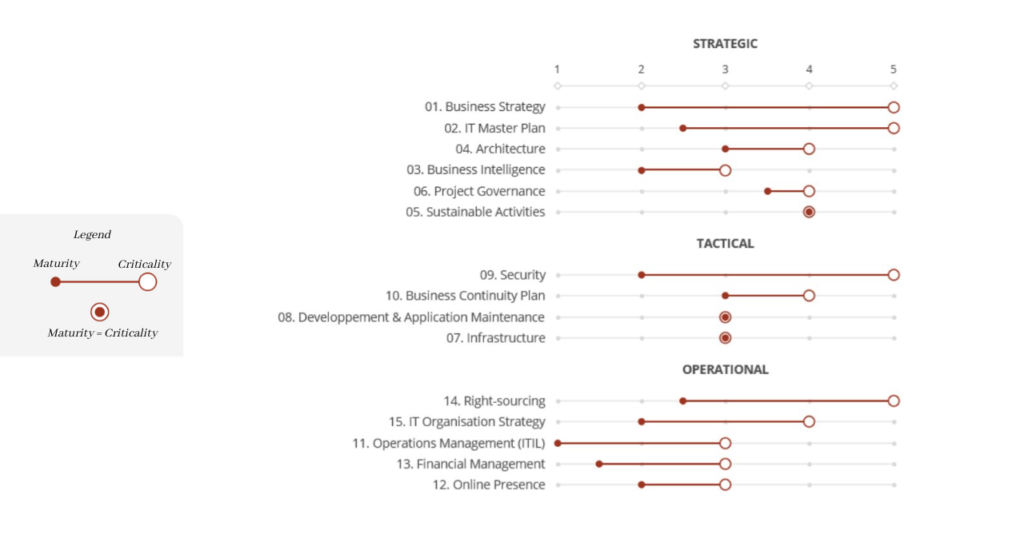

Figure 2 – Example Maturity/Criticality Indicators
Depending on the criticality of each theme for the organization, it will now be a question of identifying improvement initiatives on these best IT practices and/or identifying transformation projects (human-process-technologies). Improvement initiatives will mainly focus on best practices such as IT financial management, information asset management, right sourcing strategies, cyber risk management, architecture, etc. Transformation projects are focused on more robust initiatives such as the implementation of digital solutions, the start of a complete cybersecurity program, a business recovery plan, etc. Each of the improvement projects or ideas will be documented in terms of the potential value it can bring to the organization.
Step 4: prioritization and drafting
It is at this stage that each improvement idea or transformation project is discussed with the management of the organization. A prioritization workshop is carried out. During this workshop, prioritization is done by discussing the potential value brought by the idea or project, as well as the speed/ease of deploying the idea or project. The following prioritization tool can be used to facilitate discussion and note taking.
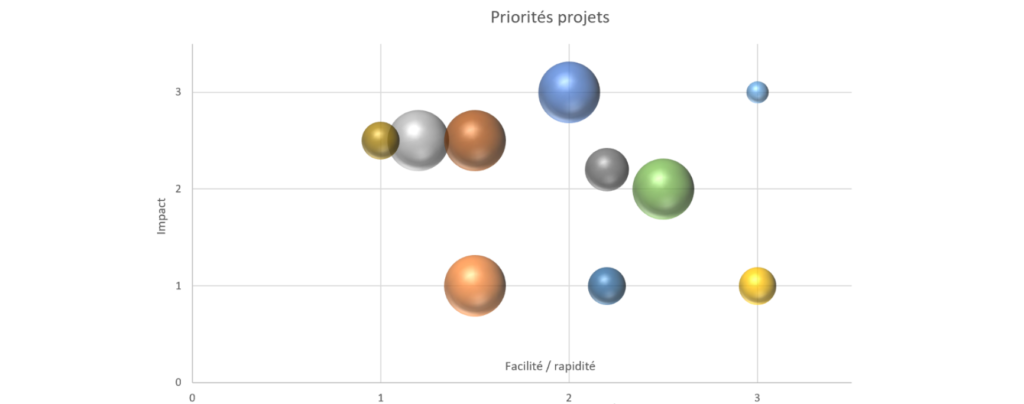
Figure 3 – Prioritization diagram
Top right projects should be prioritized. Project prerequisites (predecessor projects) are also identified. The IT master plan can now be drawn and the report written.
Step 5: the executive presentation
At this stage, it is a question of integrating the comments of the leaders and then formalizing the executive presentation. The executive presentation will provide a summary of the maturity/criticality assessment of the 15 IT governance themes, a summary of the projects, the project deployment plan and a budget overview.
Advantages of the master plan: a real tool for organizations
Once completed, the IT master plan brings several benefits to the organization:
- Visibility: It provides clear visibility on information technology and how it will contribute to the organization’s strategy over the next few years.
- Risk management: The IT master plan allows organizations to mitigate information technology risks, through its components of technological debt, IT security and succession plans.
- A reference tool: Reference will be made to the master plan to validate each of the major IT decisions, particularly those related to budget planning.
- Clear priorities: The IT master plan, through its various areas of development, presents the main priorities of information technology.
To succeed with an IT master plan, senior management must fully perceive its value and integrate it into the organization’s strategy. This plan must then be carried out by experts who have already succeeded in the exercise in many other organizations. These IT experts bring their experience, work closely with management and represent a direct extension of management on IT aspects.
Finally, it is important that the IT master plan be clear about its ultimate goals, including a list of technology investments that the organization considers to be priorities to contribute to the success of the organization. However, the plan should also include assessments of the organization’s current IT budget and assign project-specific resources and responsibilities within the IT department to achieve these goals.
Click here to learn more about Eficio’s CIO 360 offer.

